Healthy cria and calves are priceless.
Quickly identify immunodeficient cria or calves with IgG testing.
Armed with no antibodies, calves and cria are naturally at risk for infection and disease. Immunoglobulin (IgG) testing is used to quickly and accurately detect low IgG levels in order to immediately begin treatment of immunodeficient calves before serious complications arise. Early testing is preferable because delaying increases the risk of sickness for the cria and calf with Failure of Passive Transfer (FPT), making the results less effective for illness prevention.
Camelid IgG is run the same way as our Equine foal IgG tests.
Checkout this video on running an IgG test with our cube reader.
Benefits.
Our diagnostic products provide important data:
- Test on-site and get results in ten minutes.
- Tests are easy to use and interpret.
- Test IgG and treat low levels immediately.
- No refrigeration required.
- Tests remain accurate and reliable over their long shelf life (2+ years).
How to run an IgG test.
A. Obtain blood sample and run IgG test.
Step 1
Add 10 µL whole blood (or 5µL sera) to a dilution bottle and mix.
Step 2
With new tip add 10 µL from the diluted sample in the dilution bottle to the cassette.
Step 3

Add 3 drops from buffer B bottle.
Step 4
Wait 10 minutes.
B. Examine IgG test results.
Visual
Cassette Visual result
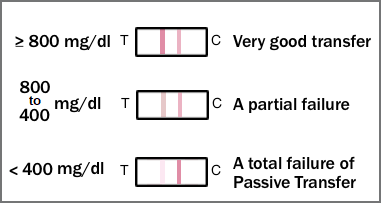
By examining the line intensities one can determine the need for supplementation. When test line intensity is much greater than control line intensity, this indicates a very good transfer (> 800 mg/dl). When the test and control lines have similar intensities, this indicates a partial failure (800 to 400 mg/dl). A weak test line compared to the control line indicates a total failure (400 mg/dl).
Quantitative
Cube reader result

The Cube Reader generates a numerical value result (in mg/dl) by interpreting the line intensities based on an internal standard curve.
Exploring Camelid IgG: Insights from Scientific Research and Lateral Flow Testing
This study, published in the American Journal of Veterinary Research in July 2000 Focuses on the passive transfer of colostral immunoglobulin G (IgG) in neonatal llamas and alpacas. It reveals that llamas and alpacas are born severely hypogammaglobulinemic, emphasizing the critical role of colostral intake in achieving adequate serum IgG concentrations. The research indicates that peak serum IgG concentrations develop between days 1 and 2 after birth, with no significant difference observed between llamas and alpacas. The optimal sampling time for assessing passive transfer status is recommended to be between 1 and 2 days postpartum. The study also addresses mortality rates associated with failure of passive transfer and suggests a threshold IgG concentration of 1,000 mg/dl at 48 hours of age as indicative of adequate passive transfer. Overall, the findings provide valuable insights into passive transfer management in these species.
This 2013 article by the Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation Using Cornell's samples emphasizes the importance of accurate measurement of immunoglobulin levels, particularly in diagnosing failure of passive transfer (FPT) in crias. The study aimed to assess the comparability of three commercially available immunologic assays for measuring serum immunoglobulin G (IgG) in alpacas and their precision. Samples from 91 alpacas were analyzed using radial immunodiffusion (RID) and two immunoturbidimetric (IT) assays. Results showed significant differences in IgG concentrations between the assays, with the RID and one IT assay yielding higher values than the other IT assay. Discordant results were observed in 1–17% of samples at an IgG threshold of 10 g/l. Electrophoresis revealed differences in assay standards, impacting results. The study suggests caution in interpreting camelid IgG data and highlights the need for standardized assays in diagnosing failure of passive transfer (FPT) in crias.
Our IgG tests utilize a lateral flow (LF) method, known for its high accuracy and stability, ensuring reliable results in assessing the transfer of immunity in neonatal crias. The results from our IgG tests align with the values found in the study above. LF tests are superior to radio immunodiffusion and immunoturbidimetric assays due to their simplicity, rapidity, portability, and ability to provide accurate results without the need for specialized equipment or extensive training.
Browse our store for camelid testing products.

